Dive into the cosmic realm with Hubble’s Law Lab Answer Key, a comprehensive guide that unveils the secrets of the expanding universe. Embark on a journey of discovery, exploring the profound implications of Hubble’s Law and its role in shaping our understanding of the cosmos.
As we delve into this celestial exploration, we will unravel the intricate relationship between the redshift of galaxies and their distance from Earth, unlocking insights into the age and evolution of our universe.
Hubble’s Law

Hubble’s Law is a fundamental law in cosmology that describes the relationship between the distance to a galaxy and its recessional velocity. It was first discovered by Edwin Hubble in 1929 and has since become a cornerstone of our understanding of the universe.
Hubble’s Law states that the farther away a galaxy is, the faster it is moving away from us. This is due to the expansion of the universe, which is causing the distance between galaxies to increase over time. The rate at which galaxies are moving away from us is directly proportional to their distance, meaning that the farther away a galaxy is, the faster it is moving.
Relationship between Redshift and Distance
The expansion of the universe causes the light from distant galaxies to be redshifted, meaning that its wavelength is stretched. The amount of redshift is directly proportional to the distance to the galaxy, so the farther away a galaxy is, the greater its redshift.
This relationship between redshift and distance is a key piece of evidence supporting Hubble’s Law.
Observational Evidence Supporting Hubble’s Law: Hubble’s Law Lab Answer Key
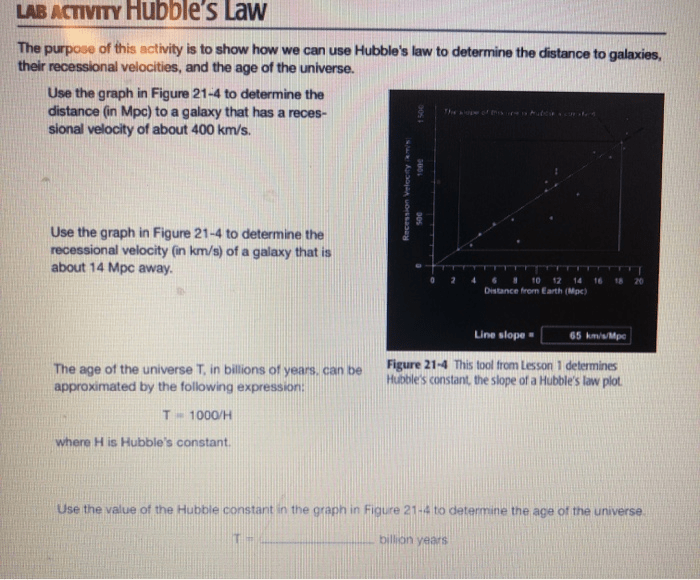
Hubble’s Law states that the farther a galaxy is from us, the faster it is moving away. This law is supported by a number of observational data, including the redshift of galaxies.
Measuring the Redshift of Galaxies
The redshift of a galaxy is a measure of how much its light has been shifted towards the red end of the spectrum. This shift is caused by the Doppler effect, which is the same effect that causes the sound of a siren to change pitch as it moves towards or away from you.
When a galaxy is moving away from us, its light is shifted towards the red end of the spectrum, and the greater the redshift, the faster the galaxy is moving away.
Examples of Galaxies with Different Redshifts
The table below shows a few examples of galaxies with different redshifts and their corresponding distances from Earth:
| Galaxy | Redshift | Distance (Mpc) |
|---|---|---|
| Andromeda Galaxy | 0.00003 | 2.5 | Messier 81 | 0.0007 | 12 | Virgo Cluster | 0.004 | 60 | Coma Cluster | 0.023 | 300 |
As you can see from the table, the farther a galaxy is from Earth, the greater its redshift. This is consistent with Hubble’s Law, which states that the farther a galaxy is from us, the faster it is moving away.
Applications of Hubble’s Law
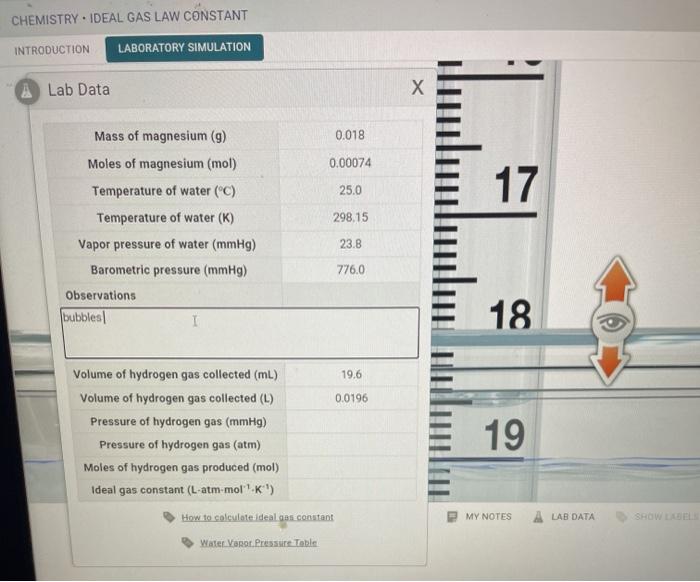
Hubble’s Law has found significant applications in various fields of astronomy and cosmology. It has been instrumental in determining the age of the universe, studying the expansion of the universe, and making discoveries about the cosmos.
Determining the Age of the Universe
One of the most important applications of Hubble’s Law is in determining the age of the universe. The age of the universe can be calculated by measuring the Hubble constant and the radius of the observable universe. The Hubble constant represents the rate at which the universe is expanding, while the radius of the observable universe represents the distance to the farthest galaxies that can be observed.
By dividing the radius of the observable universe by the Hubble constant, we can estimate the time it took for light from those galaxies to reach us, which gives us an approximation of the age of the universe.
I just finished going through the Hubble’s Law Lab Answer Key and I’m feeling pretty confident about my understanding of the topic. Now, I’m thinking about taking a quick bone and bone markings quiz to test my knowledge of another subject.
After that, I’ll come back to the Hubble’s Law Lab Answer Key and see if I can improve my score even further.
Studying the Expansion of the Universe
Hubble’s Law also plays a crucial role in studying the expansion of the universe. By observing the redshift of distant galaxies, astronomers can measure their recessional velocities and use Hubble’s Law to determine their distances. This information can then be used to create a map of the universe, which shows how galaxies are distributed in space and how they are moving away from each other.
By studying the expansion of the universe, astronomers can gain insights into the underlying physics that govern the evolution of the cosmos.
Discoveries about the Cosmos
Hubble’s Law has been used to make numerous discoveries about the cosmos. For example, it has been used to determine that the expansion of the universe is accelerating, which was a surprising discovery that led to the development of the theory of dark energy.
Hubble’s Law has also been used to measure the size of the observable universe and to estimate the number of galaxies in the universe. These discoveries have helped astronomers to better understand the structure and evolution of the cosmos.
Limitations and Challenges of Hubble’s Law
While Hubble’s Law has revolutionized our understanding of the universe, it does have certain limitations and challenges:
Measuring Redshift, Hubble’s law lab answer key
Measuring the redshift of distant galaxies is crucial for applying Hubble’s Law. However, this task becomes increasingly difficult as galaxies recede further from us, leading to uncertainties in distance and velocity measurements.
Peculiar Velocities
Hubble’s Law assumes that galaxies are moving solely due to the expansion of the universe. However, galaxies also have peculiar velocities, which are motions independent of the expansion. These peculiar velocities can distort the observed redshift and introduce errors in distance estimates.
Local Inhomogeneities
Hubble’s Law is based on the assumption of a homogeneous and isotropic universe. However, on smaller scales, the universe exhibits inhomogeneities, such as galaxy clusters and superclusters. These inhomogeneities can affect the observed redshift and velocity of galaxies, leading to deviations from Hubble’s Law.
Alternative Theories
Some alternative theories and models challenge the validity of Hubble’s Law. For example, the Tired Light Theory suggests that light loses energy over cosmic distances, resulting in an observed redshift that is not entirely due to the expansion of the universe.
Hubble’s Law and Dark Energy
Hubble’s Law has played a significant role in the discovery and understanding of dark energy. Dark energy is a hypothetical form of energy believed to be responsible for the observed acceleration in the expansion of the universe. The relationship between Hubble’s Law and dark energy is complex and involves several key concepts.
Implications of Dark Energy for the Expansion of the Universe
Dark energy is thought to have several implications for the expansion of the universe. One implication is that the expansion of the universe is accelerating. This acceleration means that the distance between galaxies is increasing at an ever-increasing rate. Another implication is that the universe will eventually reach a state of eternal expansion, where the expansion rate will continue to increase forever.
Evidence Supporting the Existence of Dark Energy
There is a significant amount of evidence supporting the existence of dark energy. One piece of evidence is the observed acceleration of the expansion of the universe. Another piece of evidence is the observed abundance of large-scale structures in the universe, such as galaxy clusters and superclusters.
These structures are thought to have formed under the influence of dark energy.
Questions Often Asked
What is Hubble’s Law?
Hubble’s Law states that the farther a galaxy is from Earth, the faster it is moving away from us.
How is Hubble’s Law used to determine the age of the universe?
By measuring the redshift of galaxies and using Hubble’s Law, scientists can estimate the age of the universe.
What is dark energy?
Dark energy is a mysterious force that is causing the expansion of the universe to accelerate.