A certain car battery with a 12.0 V EMF is a crucial component in modern vehicles, providing the electrical power necessary for starting, ignition, and powering various systems. This article delves into the intricacies of this battery, exploring its specifications, design, performance, applications, and safety considerations, offering valuable insights for automotive enthusiasts and professionals alike.
Battery Specifications and Properties: A Certain Car Battery With A 12.0 V Emf
A car battery is an essential component of a vehicle’s electrical system, providing power for starting the engine and powering electrical accessories. A typical car battery has a 12.0 V electromotive force (EMF), which is the voltage it can deliver under ideal conditions.
The voltage range of car batteries typically varies from 12.6 V when fully charged to around 11.5 V when discharged.
EMF is a measure of the electrical potential difference between the battery’s terminals. It is related to the battery’s voltage by the equation EMF = V – Ir, where V is the terminal voltage, I is the current flowing through the battery, and r is the internal resistance of the battery.
When the battery is not connected to a load, the terminal voltage is equal to the EMF.
Battery Design and Construction

A car battery typically consists of six cells connected in series, each producing approximately 2.1 V. Each cell contains a positive plate made of lead dioxide (PbO2) and a negative plate made of spongy lead (Pb). The plates are immersed in an electrolyte solution, which is a mixture of sulfuric acid (H2SO4) and water.
Separators made of porous material are placed between the plates to prevent them from touching and short-circuiting.
Different types of car batteries exist, including lead-acid batteries, lithium-ion batteries, and AGM batteries. Lead-acid batteries are the most common type, and they are relatively inexpensive and have a long lifespan. Lithium-ion batteries are more expensive but offer higher energy density and a longer lifespan.
AGM batteries are a newer type of battery that uses a glass mat separator instead of a liquid electrolyte, making them more resistant to vibration and spills.
Battery Performance and Maintenance
The performance of a car battery is affected by several factors, including temperature, discharge rate, and age. High temperatures can reduce battery life, while low temperatures can make it difficult for the battery to start the engine. High discharge rates, such as those caused by using multiple electrical accessories simultaneously, can also reduce battery life.
As a battery ages, its capacity to hold a charge decreases.
To maintain battery health and extend its lifespan, it is important to keep the battery clean and free of corrosion. The terminals should be periodically cleaned with a wire brush or sandpaper. The battery should also be tested regularly to ensure that it is still providing sufficient power.
If the battery is not performing as expected, it should be replaced.
Battery Applications and Uses
Car batteries are primarily used to start the engine and power electrical accessories in vehicles. When the ignition key is turned, the battery provides the power needed to start the engine. Once the engine is running, the alternator takes over the task of powering the electrical system and recharging the battery.
Car batteries are used in a wide range of vehicles, including cars, trucks, motorcycles, and boats. The size and capacity of the battery will vary depending on the size and power requirements of the vehicle.
Safety Considerations and Precautions
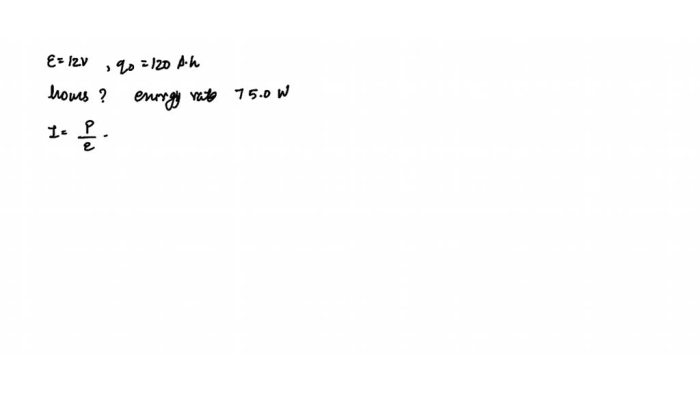
Car batteries contain sulfuric acid, which is a corrosive substance. It is important to handle and use car batteries with care to avoid injury. When working with a car battery, it is important to wear protective gear, including gloves and eye protection.
Avoid contact with the battery terminals, as this can cause a short circuit.
Car batteries should be stored in a cool, dry place. They should be kept away from sources of heat and open flames. When disposing of a car battery, it is important to follow local regulations for hazardous waste disposal.
FAQ Summary
What is the significance of a 12.0 V EMF in a car battery?
A 12.0 V EMF (electromotive force) is the electrical potential difference between the positive and negative terminals of a car battery when it is not connected to a circuit. This EMF provides the driving force for the flow of electrons when the battery is connected to a load, enabling it to power various electrical systems in the vehicle.
What are the typical voltage ranges of car batteries?
While a 12.0 V EMF is the nominal voltage for most car batteries, the actual voltage can vary depending on the battery’s state of charge and the load it is powering. A fully charged battery may have a voltage of around 12.6 V, while a discharged battery may drop to around 11.5 V.
When the battery is supplying power to electrical systems, the voltage may drop slightly due to internal resistance.
How are EMF, voltage, and electrical potential related?
EMF, voltage, and electrical potential are all closely related concepts. EMF is the potential difference between the terminals of a battery when no current is flowing, while voltage is the potential difference between two points in a circuit when current is flowing.
Electrical potential is the amount of electrical energy stored per unit charge at a given point in a circuit.