Accounting what the numbers mean 13th edition – Accounting What the Numbers Mean, 13th Edition, provides a comprehensive and engaging exploration of the fundamental principles and practices of accounting. This authoritative guide empowers readers to decipher the language of business, unlocking the secrets of financial statements and empowering them to make informed decisions.
Delving into the intricacies of accounting, this text unravels the complexities of financial reporting, equipping readers with the tools to analyze and interpret financial data with confidence. Through a systematic approach, readers will gain a deep understanding of the accounting cycle, ethical considerations, and advanced accounting topics.
Introduction: Accounting What The Numbers Mean 13th Edition
Accounting is the process of recording, classifying, summarizing, and interpreting financial transactions to provide information that is useful for decision-making.
Financial statements are the primary means of communicating accounting information to external users. They provide a snapshot of a company’s financial health and performance.
Accountants play a vital role in interpreting and analyzing financial data. They help businesses understand their financial position, make informed decisions, and comply with regulatory requirements.
Basic Accounting Concepts

The accounting equation is the foundation of accounting. It states that Assets = Liabilities + Equity.
Assets are anything owned by a company that has economic value. Liabilities are debts that a company owes to others. Equity is the residual interest in a company’s assets after deducting its liabilities.
Revenue is the income that a company earns from its operations. Expenses are the costs that a company incurs in generating revenue.
Financial Statements
The balance sheet provides a snapshot of a company’s financial position at a specific point in time.
The income statement shows a company’s revenues and expenses over a period of time.
The statement of cash flows shows how a company generates and uses cash.
Accounting Cycle
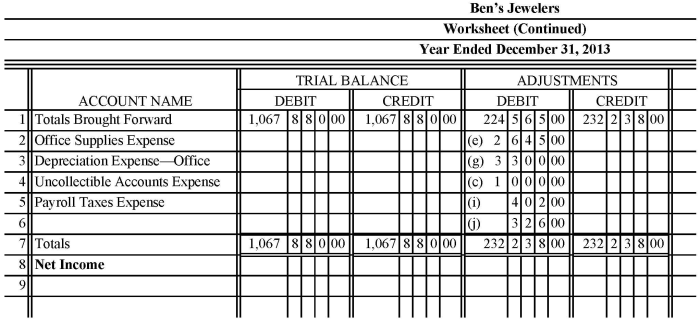
The accounting cycle is the process of recording, classifying, summarizing, and interpreting financial transactions.
The accounting cycle begins with the recording of transactions in a journal. The journal entries are then posted to the ledger, which is a collection of accounts that track the changes in a company’s financial position.
At the end of the accounting period, the ledger is used to prepare financial statements.
Advanced Accounting Topics

Inventory valuation is the process of determining the value of a company’s inventory.
Depreciation and amortization are accounting methods used to allocate the cost of long-term assets over their useful lives.
Long-term debt is a type of financing that a company uses to fund its operations.
Ethical Considerations in Accounting
Accountants have a responsibility to act ethically and with integrity.
Ethical challenges that accountants may face include conflicts of interest, pressure to meet financial targets, and the need to maintain confidentiality.
Accountants can maintain their ethical integrity by following ethical guidelines, seeking professional advice, and reporting any unethical behavior.
Question & Answer Hub
What is the purpose of financial statements?
Financial statements provide a comprehensive overview of a company’s financial health, summarizing its assets, liabilities, equity, revenues, and expenses.
What is the role of accountants in financial reporting?
Accountants play a crucial role in ensuring the accuracy and reliability of financial statements by interpreting and analyzing financial data, adhering to accounting standards, and maintaining ethical integrity.
What are the key components of the accounting equation?
The accounting equation, Assets = Liabilities + Equity, serves as the foundation of accounting and represents the relationship between a company’s resources, obligations, and ownership interest.