Identify the letter that indicates a Schwann cell, delving into the intricacies of the nervous system’s essential cellular components. Schwann cells play a pivotal role in maintaining the health and functionality of our nervous system, and understanding their significance requires a thorough examination of their structure, function, and the specific letter used to represent them in scientific literature.
This exploration will provide a comprehensive overview of Schwann cells, their unique characteristics, and the significance of their identification in biomedical research.
Schwann Cells: Identify The Letter That Indicates A Schwann Cell
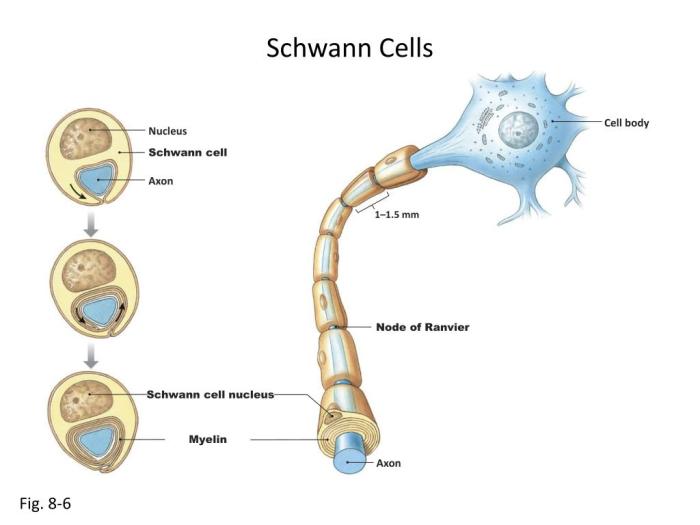
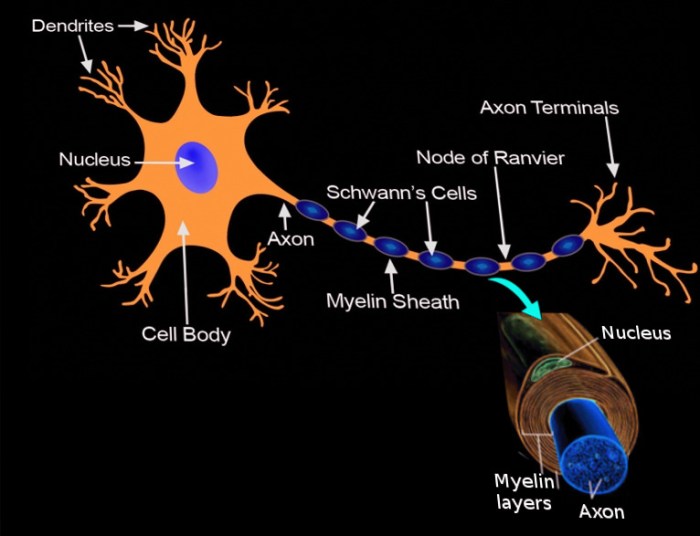
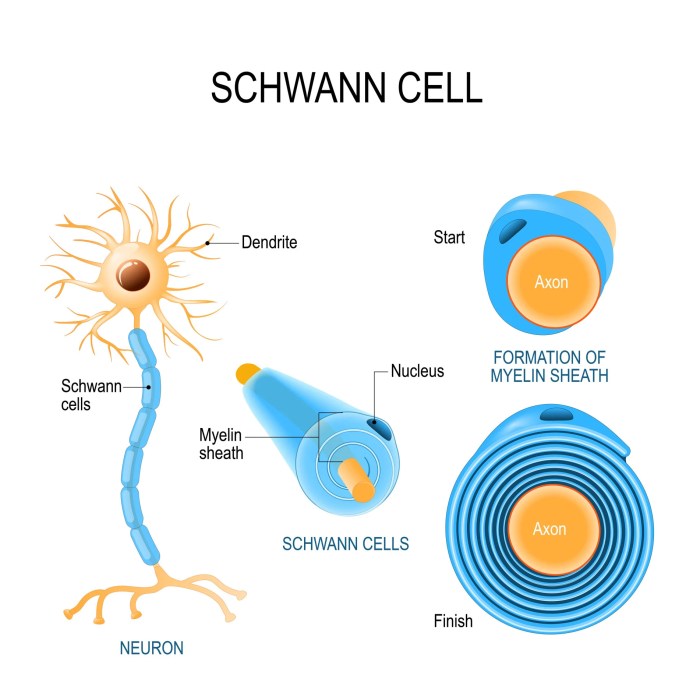
Schwann cells are specialized glial cells that play a crucial role in the development, function, and repair of the peripheral nervous system. They are responsible for forming the myelin sheath, an insulating layer that surrounds and protects the axons of neurons.Schwann
cells have a unique structure that enables them to perform their functions effectively. They have a large, flat cell body with a centrally located nucleus. Extending from the cell body are numerous processes that wrap around the axons of neurons, forming the myelin sheath.
The myelin sheath acts as an insulator, preventing the leakage of electrical signals and increasing the speed of signal transmission along the axon.
Process of Schwann Cell Myelination
The process of Schwann cell myelination is complex and highly regulated. It involves several distinct steps:
- Contact and alignment:Schwann cells initially make contact with the axon and align themselves along its length.
- Wrap and fold:The Schwann cell processes then wrap around the axon multiple times, forming a multi-layered myelin sheath.
- Compaction:The layers of myelin are compacted together, squeezing out the cytoplasm and creating a tightly packed sheath.
- Formation of Schmidt-Lanterman incisures:The myelin sheath is not continuous but is interrupted by gaps called Schmidt-Lanterman incisures. These gaps allow for the diffusion of nutrients and waste products between the Schwann cell and the axon.
Letter Indicating Schwann Cells
In scientific literature, the letter “S” is commonly used to indicate Schwann cells. This letter is used as an abbreviation for “Schwann” and is often used in conjunction with other abbreviations to describe different types of Schwann cells. For example, “SC” stands for Schwann cell, “S100” refers to a specific protein expressed by Schwann cells, and “p75” denotes a receptor protein found on Schwann cells.The
use of the letter “S” to indicate Schwann cells is due to their historical discovery and characterization by the German physiologist Theodor Schwann. In his seminal work in the 19th century, Schwann described the role of these cells in the formation of the myelin sheath and their importance in the function of the peripheral nervous system.
Examples of Use, Identify the letter that indicates a schwann cell
Here are some examples of where the letter “S” is used to indicate Schwann cells in scientific writing:
- The study investigated the expression of S100 protein in Schwann cells (SCs) during nerve regeneration.
- The p75 receptor is a marker for Schwann cells (S) and is involved in Schwann cell proliferation and differentiation.
- Schwann cells (S) play a crucial role in the development and maintenance of the peripheral nervous system.
Schwann Cell Markers
Specific markers are used to identify and characterize Schwann cells in research and clinical settings. These markers are proteins or other molecules that are expressed specifically by Schwann cells or are enriched in their membranes or cytoplasm.
- S100:S100 is a calcium-binding protein that is expressed in high levels in Schwann cells. It is a widely used marker for Schwann cell identification and can be detected using immunohistochemistry or flow cytometry.
- p75:p75 is a neurotrophin receptor that is expressed on Schwann cells. It is involved in Schwann cell proliferation, differentiation, and survival. p75 can be used as a marker to identify Schwann cells in culture or in tissue sections.
- GFAP:Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) is an intermediate filament protein that is expressed in Schwann cells. It is commonly used as a marker for Schwann cells in pathological conditions, such as Schwann cell tumors.
- Myelin proteins:Myelin proteins, such as myelin basic protein (MBP) and myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG), are specific to myelinating cells. These proteins can be used as markers to identify Schwann cells that are actively myelinating axons.
These markers are essential for Schwann cell research, allowing scientists to study the development, function, and pathology of these cells. They are also used in clinical diagnostics to identify Schwann cell tumors and other Schwann cell-related disorders.
Essential FAQs
What is the function of Schwann cells?
Schwann cells are responsible for myelination, a process that insulates nerve fibers and facilitates efficient electrical signal transmission.
Why is it important to identify Schwann cells?
Identifying Schwann cells is essential for studying their role in nervous system development, function, and disease.
What are some disorders associated with Schwann cells?
Schwann cell disorders include neurofibromatosis, Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, and Guillain-Barré syndrome.